Welcome to BecA bioinformatics page
This portal serves to introduce various bioinformatics resources and tools to aid ABCF placements analyse and intepret their data.
For presentations and slides for training and tutorials given by BecA Research assosciates, please click here
Bioinformatics Modules
Introduction to Bioinformatics
Introduction to bioinformatics, Definitions and glossary, software and bibliographic databases; Guides and tutorials

Linux for biology
This module is designed for scientists hoping to analyze genomic datasets, but who have no experience with the UNIX computing environment or common genomic analysis tools.

Database and searching
Nucleic acid and protein sequences are stored in sequence databases. These are open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations.
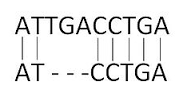
Pairwise and Multiple sequence alignments
Sequence alignment is a widely used bioinformatic technique to try to align several related sequences to find residues / bases which are conserved between sequences and which are variable. Conserved residues may be an essential part of the active site of an enzyme for example, and variable residues could be part of a 'generic' alpha helix.
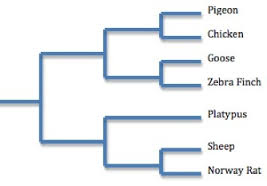
Phylogeny and evolutionary relationships
A phylogeny, or evolutionary tree, represents the evolutionary relationships among a set of organisms or groups of organisms, called taxa (singular: taxon).

Population Genetics
Population genetics is the study of the distributions and changes of allele frequencies in a population, as it is subject to four main processes: mutation, selection, genetic drift and genetic recombination.
Advanced: Next Generation Sequence- Data analysis
Functional genomics is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic and transcriptomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects and RNA-seq) to describe gene (and protein) functions and interactions.

Advanced: Genotyping by Sequencing
Genotyping by sequencing is cost-effective for populations with complex genomes or limited available resources.